Organotinchemie: verschil tussen versies
k Nieuwe pagina aangemaakt met 'right|150px In de strikte zin van het woord worden in de '''organotinchemie''' verbindingen bestudeerd wa...' |
(geen verschil)
|
Versie van 11 nov 2010 18:50

In de strikte zin van het woord worden in de organotinchemie verbindingen bestudeerd waarin een direkte binding voorkomt tussen koolstof en tin. In een minder strikt verstaan van de term worden ook organische reacties bestudeerd waarbij tin een essentiele rol speelt. In analogie met de silanen worden organotinverbindingen die afgeleid zijn van alkanen ook wel stannanen genoemd. Tin is een metaal, de organotinchemie is daarmee een subdiscipline van de organometaalchemie.[1] In 1849 werd de eerste organotinverbinding beschreven door Edward Frankland: diethyltindiiodide. Organotinverbindingen worden commercieel toegepast bij het neutraliseren van waterstofchloride in PVC en als biocide. Tributyltinoxide is veel gebruikt bij het beschermen van hout. Tributyltinverbindingen zijn veel toegepast in de mariene antifoulingverven. Uiteraard zijn antifoulingstoffen giftig, maar de gebruikte tinverbindingen zijn dat voor veel meer zeeorganismen dan waar antofouling voor wordt toegepast.[2]. Wereldwijd is daarom door de Internationale Maritieme Organisatie een verbod op het gebruik van antifouling op basis van tin afgekondigd. n−Butyltintrichloride wordt toegepast bij het vormen van een laagje tin(IV)oxide op glaswerk via Chemical vapor deposition.
Synthese van organotinverbindingen
Organotinverbindingen kunnen gemaakt worden in een Grignardreactie met een tinhalide zoals Tin(IV)chloride. Ook tinhalides waaraan een deel van de chlooratomen al vervangen is door organische groepen ondergaan deze reactie. Een voorbeeld van een dergelijke synthese is die van tributyl-[(Z)-5-phenyl-2-penten-2-yl]stannane:[3] [4]
De Wurtz-achtige reactie tussen alkylnatriumverbindingen en tinhalides levert tetraorganotinverbindingen. Een andere benadering is de uitwisselingsreactie tussen tinhalides en organoaluminiumverbindingen (AlR3). Triorganotinhalides worden verkregen via de Kocheshkov redistributiereactie.
Reacties van organotinverbindingen
Belangrijke reacties van organotinverbindingen zijn onder andere
- de Stille-reactie (palladium is katalysator in de koppelingsreactie tussen sp2-gehybridizeerde organische halides):
- organostannaanaddities, de nucleophiele additie van stannanen met een allyl-, allenyl-, of propargylgroep aan aldehydes en imines.
Use and toxicity
- Tetraorganotins are very stable molecules with low toxicity and low biological activity. They are unusable as biocides, but they can be metabolized to toxic triorganotin compounds. They are used as starting materials for catalysts.
- Triorganotins are very toxic. Tri-n-alkyltins are phytotoxic and therefore cannot be used in agriculture. Depending on the organic groups, they can be powerful bactericides and fungicides. Tributyltins are used as industrial biocides, eg. as antifungal agents in textiles and paper, wood pulp and paper mill systems, breweries, and industrial cooling systems. Tributyltins are also used in marine anti-fouling paint. Triphenyltins are used as active components of antifungal paints and agricultural fungicides. Other triorganotins are used as miticides and acaricides.
- Diorganotins have no antifungal activity, low toxicity, and low antibacterial activity, except for diphenyltins. They are used in polymer manufacturing, as PVC heat stabilizers, catalysts, in the manufacturing of polyurethane and silicone curing. DBT is however immunotoxic, and a recent paper suggests a link to auto-immune related diseases.[5]
- Monoorganotins have no biocidal activity and their toxicity to mammals is very low. Methyltin, butyltin, octyltin and monoestertins are used as PVC heat stabilizers.
- Many different organotin complexes are being studied in anticancer therapy, observing that their cytotoxicity and selectivity towards cancer cell is higher than that of cisplatin.[6]
Compounds
Organotin compounds are used commercially in a wide range of applications such as biocides, insecticides, chemical intermediates and as catalysts.
- Organotin compounds
-
Tetrabutyltin starting material for the di- and tributyl compounds
-
Tributyltin oxide, a colorless to pale yellow liquid used in wood preservation
-
Triphenyltin chloride, a white crystalline solid, used as a biocide and an intermediate in chemical synthesis
-
Trimethyltin chloride also a biocide
-
Triphenyltin hydroxide, an off-white powder, used as a fungicide and to sterilize insects
-
Azocyclotin, a colorless crystalline solid, used as a long-acting acaricide for control of spider mites on plants
-
Hexamethylditin used as an intermediate in chemical synthesis
Other classifications
Polystannanes are polymeric stannanes of the type (SnR2)n
Stannoles are the structural analogs of pyrrole. Unsaturated organostannanes also exist: stannenes are compounds of the type RRC=SnRR with a formal double bond (also see stannabenzene) and distannenes have a tin to tin double bond as in RRSn=SnRR. A stannyne contains a carbon to tin triple bond and a distannyne a triple bond between two tin atoms (RSnSnR) . Tin radicals are called stannyl radicals and tin carbenes stannylenes (RSn:) [8]
Hypercoordinated stannanes
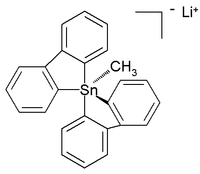
Unlike their carbon analogues, tin compounds can also be coordinated to five and even six atoms instead of the regular four. These hypercoordinated compounds usually have electronegative substituents for stabilization. Lithium pentaorganostannates were first detected and characterized in solution in 1986,[9] while in the subsequent year a six-coordinated tetraorganotin compound was reported.[10] In 2007 a crystal structure of room-temperature stable (in argon) all-carbon pentaorganostannane was reported as the lithium salt with this structure:[11]
In this distorted trigonal bipyramidal structure the carbon to tin bond lengths (2.26Å apical, 2.17Å equatorial) are larger than regular C-Sn bonds (2.14Å) reflecting its hypervalent nature.
Externe links
- National Pollutant Inventory Fact Sheet for organotins
- Industry information site
- Organotin chemistry in synthesis
- EU bans certain organotin compounds in consumer products
Zie ook
- ↑ Sander H.L. Thoonen, Berth-Jan Deelman, Gerard van Koten (2004). Synthetic aspects of tetraorganotins and organotin(IV) halides. Journal of Organometallic Chemistry (689): 2145–2157.
- ↑ Gajda, M., Jancso, A. (2010). Organotins, formation, use, speciation and toxicology. Metal ions in life sciences 7, Organometallics in environment and toxicology (RSC publishing: Cambridge).
- ↑ Martin J. Stoermer, John T. Pinhey (1998). Tributyl-[(Z)-5-phenyl-2-penten-2-yl]stannane. Molecules 3: M67.
- ↑ Het Grignardreagens wordt gemaakt op basis van magnesiumkrullen en (Z)-2-bromo-5-phenyl-2-penteen in droge (=watervrije) tetrahydrofuraan. Vervolgens wordt tributyltinchloride via een buret toegevoegd totdat het reactiemengsel ontkleurt, eigenlijk een titratie. Het reactiemengsel wordt nog een uur bij kamertemperatuur geroerd, waarna het oplosmiddel met behulp van een rotavapor verwijderd wordt. Na toevoegen van diethylether, wassen met brijn, filtreren en opnieuw oplosmiddel met de rotavapor verwijderen wordt het ruwe product verkregen. Na destillatie wordt tributyl-[(Z)-5-phenyl-2-penten-2-yl]stannaan als een kleurloze olie geisoleerd.
- ↑ C Gumy et al. (2008). Dibutyltin Disrupts Glucocorticoid Receptor Function and Impairs Glucocorticoid-Induced Suppression of Cytokine Production. PLoS ONE 3. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003545.
- ↑ S. Gómez-Ruiz et al. (2008). Study of the cytotoxic activity of di and triphenyltin(IV) carboxylate complexes. Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry 102: 2087. DOI: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2008.07.009.
- ↑ Organic Syntheses, Coll. Vol. 4, p.881 (1963); Vol. 36, p.86 (1956). Link
- ↑ Organotin chemistry 2004 Alwyn George Davies ISBN-10: 3-527-31023-1
- ↑ Reich, Hans J. (1986). Lithium-Metalloid Exchange Reactions. Observation of Lithium Pentaalkyl/aryl Tin Ate Complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 108: 2102. DOI: 10.1021/ja00268a067.
- ↑ V. G. Kumar Das, Lo Kong Mun, Chen Wei, and Thomas C. W. Mak (1987). Synthesis, Spectroscopic Study, and X-ray Crystal Structure of Bis[3-(2-pyridyl)-2-thienyl-C,N]diphenyltin(IV): The First Example of a Six-Coordinate Tetraorganotin Compound. Organometallics 6: 10. DOI: 10.1021/om00144a003.
- ↑ Masaichi Saito, Sanae Imaizumi, Tomoyuki Tajima, Kazuya Ishimura, and Shigeru Nagase (2007). Synthesis and Structure of Pentaorganostannate Having Five Carbon Substituents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129: 10974–10975. DOI: 10.1021/ja072478.








![Tetraethyltin, boiling point 63–65° /12 mm is a catalyst [7]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/1/1e/Tetraethyltin.svg/120px-Tetraethyltin.svg.png)